Operation Midnight Hammer: Largest B-2 Strike Targets Iran
Operation Midnight Hammer targeted Iran’s nuclear sites in a history-making B-2 bomber strike using advanced deception tactics.
Pentagon Details Largest U.S. B-2 Operational Strike
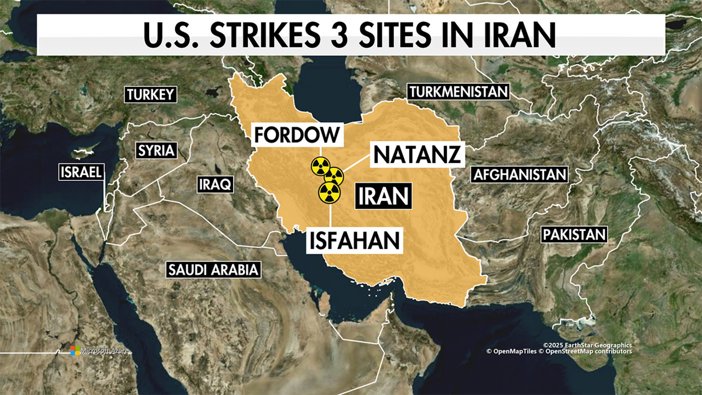
The Pentagon on Sunday unveiled comprehensive details of Operation Midnight Hammer, describing it as the largest B-2 operational strike in U.S. history. This meticulously planned mission, launched late Saturday, struck three of Iran’s most critical nuclear facilities—Fordow, Natanz, and Isfahan—using an unprecedented combination of stealth, technology, and military coordination.
Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth emphasized the calculated nature of the strike, noting that while the operation’s scope was intentionally limited, the military’s capabilities remain nearly unlimited. General Dan Caine, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, provided a step-by-step account of the operation’s planning, deception strategies, and execution.
Stealth Bombers and Deception Tactics Lead the Way
The operation commenced at 12:01 a.m. Saturday when B-2 Spirit stealth bombers departed Whiteman Air Force Base in Missouri. Some aircraft flew west into the Pacific as a decoy, a maneuver known only to a select group of planners and key leaders, while the primary strike force flew silently eastward, minimizing communications for maximum secrecy.
Refueled several times en route, the B-2 bombers linked up with Central Command’s escort and support aircraft in a tightly synchronized maneuver that required exact timing and precise coordination. As the main strike group entered Iranian airspace, a U.S. submarine launched more than two dozen Tomahawk land attack cruise missiles, targeting key surface infrastructure.
Support aircraft advanced ahead of the main bombers to sweep for potential enemy fighters and surface-to-air missile threats, using high-speed suppression weapons to clear a safe passage. According to Gen. Caine, the U.S. strike group encountered no resistance—“Iran's fighters did not fly, and it appears that Iran's surface-to-air missile systems did not see us throughout the mission. We retained the element of surprise.”
First-Ever Use of 30,000-Pound Bunker-Buster Bombs
The strike on Fordow nuclear facility occurred at approximately 6:40 p.m. EST. The lead B-2 dropped two GBU 57 Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP) bunker-busters, each weighing 30,000 pounds, followed by additional munitions on further aim points at Fordow and Natanz. In total, 14 MOPs were dropped, marking the first operational use of this formidable weapon. Tomahawk missiles from submarines delivered the final strikes on Isfahan.
After releasing their payloads, the B-2 bombers exited Iranian airspace and returned to Missouri without any reported shots fired at them. The mission involved more than 125 aircraft, including stealth bombers, fighters, refueling tankers, a guided missile submarine, and intelligence platforms. In all, around 75 precision-guided munitions were used.
General Caine described Operation Midnight Hammer as the “largest B-2 operational strike in U.S. history,” and the second-longest B-2 mission ever flown, surpassed only by those immediately following the September 11 attacks. “No other military in the world could have done this,” Caine said, underscoring the global reach and unmatched capability of U.S. forces.
This operation, executed from strategic planning to global action in a matter of weeks, demonstrates the United States’ ability to deliver complex, decisive blows while minimizing risk and maximizing surprise. As officials assess the mission’s impact on Iran’s nuclear infrastructure, Operation Midnight Hammer stands as a historic benchmark in modern military operations.






